Is Multicellular Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic
Introduction: Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes
Biotic components of the surround include all forms of life from minute bacteria to towering giant Sequoias. All the same, at the microscopic level, all living organisms are made up of the same bones unit – the cell.
Contents:
- Prokaryotic Prison cell
- Eukaryotic Cell
- Departure between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
As a result, the prison cell is referred to as the structural and functional unit of all living organisms.The word jail cell has its origins in Latin, and when translated, it means "small room" and was get-go observed by Robert Hooke – an English language natural philosopher in the year 1665.
He likewise compared his discovery to the cells in a honeycomb, equally they showcase a similar structure.
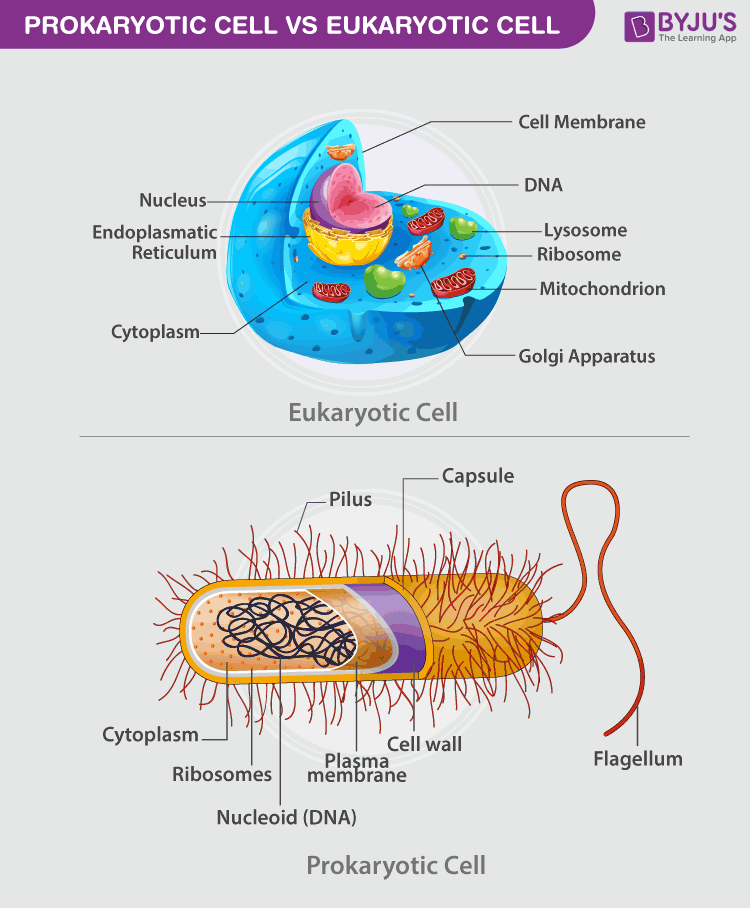
An image illustrating the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Note that the prokaryotic cell is a complete individual organism
Eventual advancements in scientific discipline and technology shed more light into the cell, with new findings and discoveries about its structure and cellular components.During the 1950s, scientists postulated the concept of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, with earlier groundwork being laid past Edouard Chatton, a French Biologist in 1925.
Anatomically, cells vary with respect to their classification, therefore, prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells differ from each other quite drastically. Read on to explore how they differ from each other.
Prokaryotic Prison cell
The term "prokaryote" is derived from the Greek discussion "pro", (meaning: before) and "karyon" (meaning: kernel). It translates to " before nuclei. "
Prokaryotes are 1 of the nigh ancient groups of living organisms on earth, with fossil records dating back to almost three.5 billion years agone.
These prokaryotesthrived in the earth's ancient surroundings, some using up chemical energy and others using the sun'southward energy. These extremophiles thrived for millions of years, evolving and adapting. Scientists speculate that these organisms gave ascension to the eukaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus. Reproduction happens through the procedure of binary fission.
Structurally, prokaryotes have a capsule enveloping their entire body, and it functions every bit a protective coat. This is crucial for preventing the process of phagocytosis (where the bacteria gets engulfed by other eukaryotic cells, such as macrophages) The pilus is a hair-similar bagginess establish on the external surface of nearly prokaryotes and it helps the organism to attach itself to diverse environments. The hair substantially resists being flushed, hence, it is as well called zipper pili. It is unremarkably observed in bacteria.
Right beneath the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides force and rigidity to the cell. Farther down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside surroundings. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also ane of the smallest components inside the prison cell.
Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assistance in cellular respiration. Most prokaryotes as well contain plasmids, which incorporate small, circular pieces of Dna. To aid with locomotion, flagella are present, though, pilus can as well serve every bit an aid for locomotion. Common examples of Prokaryotic organisms are bacteria and archaea. Also, all members of Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes.
Chief Article: Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic Prison cell
The term "Eukaryotes" is derived from the Greek word "eu", (meaning: good) and "karyon" (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to " good or true nuclei ." Eukaryotes are more than complex and much larger than prokaryotes.They include near all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
Structurally, eukaryotes possess a jail cell wall, which supports and protects the plasma membrane. The prison cell is surrounded by the plasma membrane and information technology controls the entry and go out of certain substances.
The nucleus contains Deoxyribonucleic acid, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded past the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial function in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the cosmos of energy, which is then utilized by the jail cell.
Present in only institute cells, chloroplasts are the subcellular sites of photosynthesis. The endoplasmic reticulum helps in the transportation of materials. Besides these, there are also other cell organelles that perform various other functions and these include ribosomes, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, cytoplasm, chromosomes, vacuoles and centrosomes.
Examples of eukaryotes include almost every unicellular organism with a nucleus and all multicellular organisms.
Main Article:Eukaryotic Cells
Divergence betwixt Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Though these two classes of cells are quite dissimilar, they practise possess some common characteristics. For instance, both possess cell membranes and ribosomes, but the similarities cease there. The consummate list of differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is summarized every bit follows:
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
| Type of Cell | E'er unicellular | Unicellular and multi-cellular |
| Cell size | Ranges in size from 0.ii μm – two.0 μm in bore | Size ranges from 10 μm – 100 μm in diameter |
| Cell wall | Ordinarily present; chemically complex in nature | When nowadays, chemically simple in nature |
| Nucleus | Absent. Instead, they have a nucleoid region in the cell | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present. Smaller in size and spherical in shape | Present. Comparatively larger in size and linear in shape |
| Deoxyribonucleic acid arrangement | Circular | Linear |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present, but cell organelles absent | Present, prison cell organelles present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Plasmids | Present | Very rarely found in eukaryotes |
| Ribosome | Pocket-sized ribosomes | Large ribosomes |
| Lysosome | Lysosomes and centrosomes are absent | Lysosomes and centrosomes are nowadays |
| Cell division | Through binary fission | Through mitosis |
| Flagella | The flagella are smaller in size | The flagella are larger in size |
| Reproduction | Asexual | Both asexual and sexual |
| Example | Bacteria and Archaea | Establish and Brute prison cell |
Learn more than nearly prokaryotic prison cell and eukaryotic prison cell, their differences and other related topics at BYJU'Southward Biology
Ofttimes Asked Questions
What is a Prokaryotic jail cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a archaic type of cell that is characterized by the absenteeism of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes exercise not possess membrane-bound cellular organelles. Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular.
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent-minded, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present simply in eukaryotic cells.
Some other major departure between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells are exclusively unicellular, while the same does not utilize to eukaryotic cells.
Define Jail cell?
The prison cell is the bones functional and structural unit of life. Prison cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organelles, which perform several individual functions to continue the cell alive and active.
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are nowadays both in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Compared to prokaryotes, eukaryotes accept larger ribosomes in their cells.
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells accept several unique features. Listed below are some important features:
- In structure, both animal and plant cells are quite like.
- Both possess nucleus and plasma membrane, a selectively permeable membrane of the cell.
- Both beast and found cells include membrane-jump organelles with their specialized functions.
- Creature and establish cells have vacuoles, which serve as the storage unit and maintain the shape of the cell.
- Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell. Information technology stores and provide free energy for different cellular activities and is found both in both creature and plant cells.
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic paint chosen chlorophyll and are involved in synthesizing nutrient by the process of photosynthesis.
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was showtime discovered in the yr 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in the year 1830.
Farther Reading:
-
- Competent Cells
- Divergence Between Plasmid Deoxyribonucleic acid And Chromosomal DNA
Is Multicellular Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells/
Posted by: rickettsfrinslazince.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is Multicellular Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic"
Post a Comment